
Logarithm Introduction What is Logarithm, Rules, Functions & Examples Cuemath
Sometimes a logarithm is written without a base, like this: log (100) This usually means that the base is really 10. It is called a "common logarithm". Engineers love to use it. On a calculator it is the "log" button. It is how many times we need to use 10 in a multiplication, to get our desired number. Example: log (1000) = log10(1000) = 3.

Ex 5.5, 7 Differentiate the function (log x)^x + x^log x
This is the Logarithmic Function: f (x) = log a (x) a is any value greater than 0, except 1 Properties depend on value of "a" When a=1, the graph is not defined Apart from that there are two cases to look at: Plot the graph here (use the "a" slider) In general, the logarithmic function: always has positive x, and never crosses the y-axis

How To Calculate Log X In Geometric Mean Haiper
Logarithms, like exponents, have many helpful properties that can be used to simplify logarithmic expressions and solve logarithmic equations. This article explores three of those properties. Let's take a look at each property individually. The product rule: log b ( M N) = log b ( M) + log b ( N)
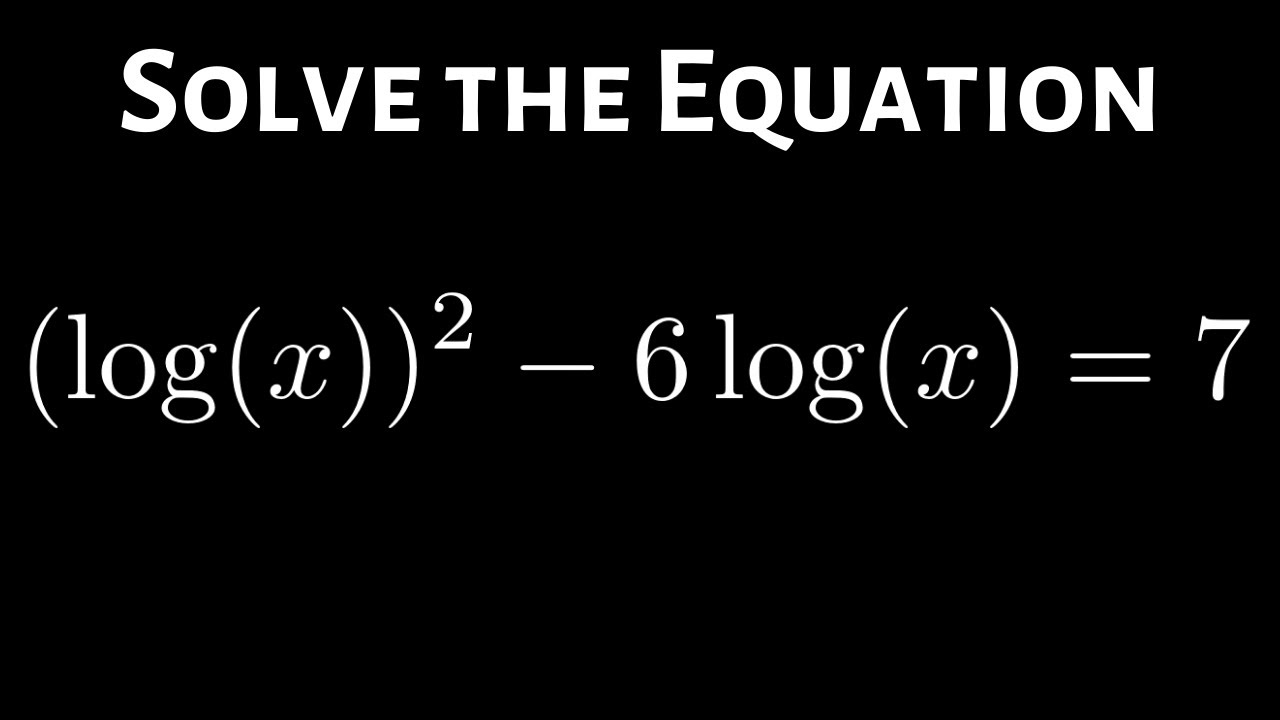
Solving the Logarithmic Equation (logx)^2 6*logx = 7 YouTube
k+1) with ∂f(x k+1) = A⊤log Ax k+1 b M k+1 = G(x k+1)−1 with inverse metric tensor as listed in Table1 x k+1 = exp x k (τv k) Increment k←k+ 1. Unlike monotone strategies that strictly ensure a decrease in the sequence of function values (f(x k)) k∈N with each iteration, this approach does not require f(x k+1) logarithm, the exponent or power to which a base must be raised to yield a given number. Expressed mathematically, x is the logarithm of n to the base b if bx = n, in which case one writes x = log b n. For example, 2 3 = 8; therefore, 3 is the logarithm of 8 to base 2, or 3 = log 2 8. In the same fashion, since 10 2 = 100, then 2 = log 10 100. 4 Answers. By definition, the log − log − function is the inverse of the exponential function. It means that, if f: R →R+ f: R → R + such that, f(f−1(x)) = x. f ( f − 1 ( x)) = x. We then define f−1 f − 1 as f−1(x) =loga x f − 1 ( x) = log a x. So, f(f−1(x)) = x ⇔ aloga x = x. f ( f − 1 ( x)) = x a log a x = x. log(a)log(x) = log(a)log(x) log ( a) l o g ( x) = log ( a) log ( x) This is essentially another way of saying what sanjab has already said, but in a way that gives it a bit more intellectual context. Its sort of the "deeper reason" why it works. So why does plog(q) qlog(p) p log ( q) = q log ( p)? log(x) Natural Language; Math Input; Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random. Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music… In mathematics, the logarithm is the inverse function to exponentiation. That means that the logarithm of a number x to the base b is the exponent to which b must be raised to produce x. For example, since 1000 = 103, the logarithm base 10 of 1000 is 3, or log10 (1000) = 3. Free Logarithms Calculator - Simplify logarithmic expressions using algebraic rules step-by-step Definition of a logarithm Generalizing the examples above leads us to the formal definition of a logarithm. log b ( a) = c b c = a Both equations describe the same relationship between a , b , and c : b is the base , c is the exponent , and a is called the argument . A helpful note This log calculator (logarithm calculator) allows you to calculate the logarithm of a (positive real) number with a chosen base (positive, not equal to 1). Regardless of whether you are looking for a natural logarithm, log base 2, or log base 10, this tool will solve your problem. Let's go through the correct application of the logarithmic properties and show why the statement is incorrect: The product rule for logarithms states that log_x (A) + log_x (B) = log_x (A * B). Suppose we have the expressions: (LogX (A) = l) and (LogX (B) = m). According to the product rule, combining these two expressions should give us: Product Formula of logarithms The product formula of logs is, log b (xy) = log b x + log b y. Derivation: Let us assume that log b x = m and log b y = n. Then by the definition of logarithm, x = b m and y = b n. Then xy = b m × b n = b m + n (by a law of exponents, a m × a n = a m + n) Converting xy = b m + n into logarithmic form, we get Logarithmic Functions. Like many types of functions, the exponential function has an inverse. This inverse is called the logarithmic function. logax = y means ay = x. where a is called the base; a > 0 and a≠1. For example, log232 = 5 because 25 = 32. log5 = - 3 because 5-3 = . To evaluate a logarithmic function, determine what exponent the. What is the Derivative of log x? The derivative of logₐ x (log x with base a) is 1/ (x ln a). Here, the interesting thing is that we have "ln" in the derivative of "log x". Note that "ln" is called the natural logarithm (or) it is a logarithm with base "e". i.e., ln = logₑ.
Ex 5.5, 7 Differentiate the function (log x)^x + x^log x

How To Find The Base Of A Logarithm (4 Key Concepts) JDM Educational

Properties of Logarithms (Part 2) Lecture 6 a^logax=x and a alogcb=blogca YouTube
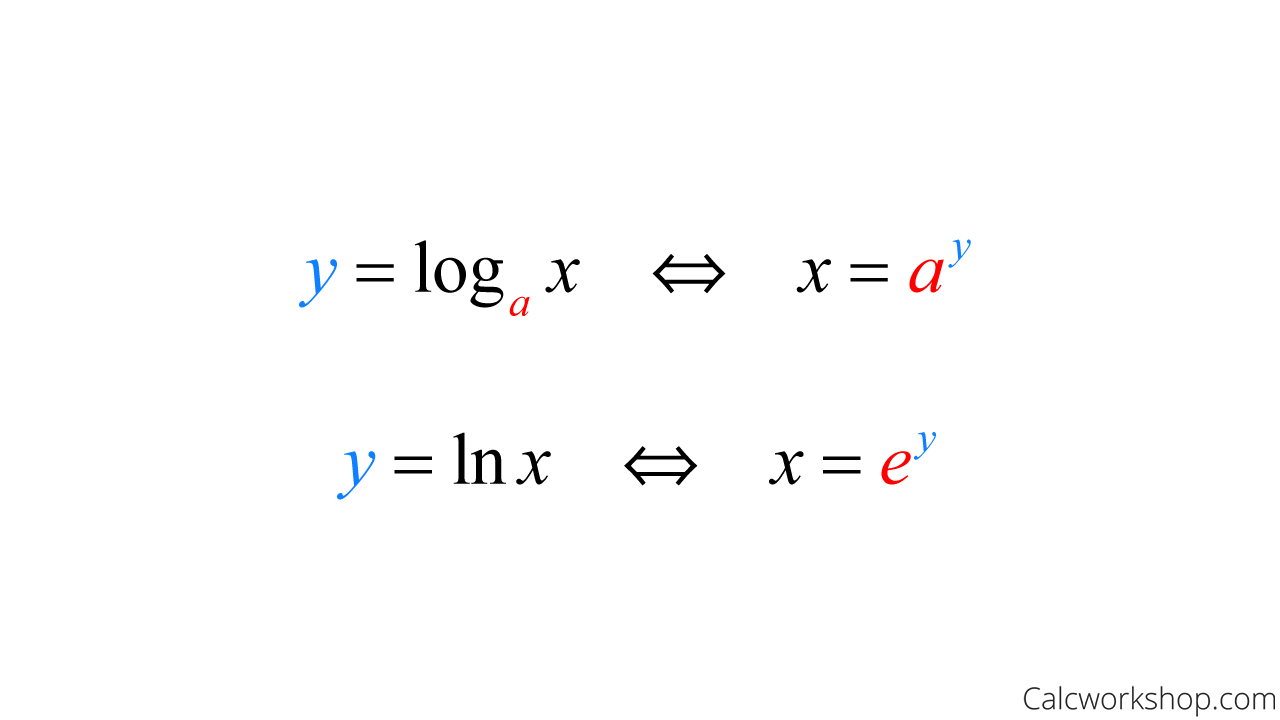
Logarithmic Function Formula

Ex 5.5, 7 Differentiate the function (log x)^x + x^log x

Ex 5.7, 9 Find second order derivatives of log (log x)
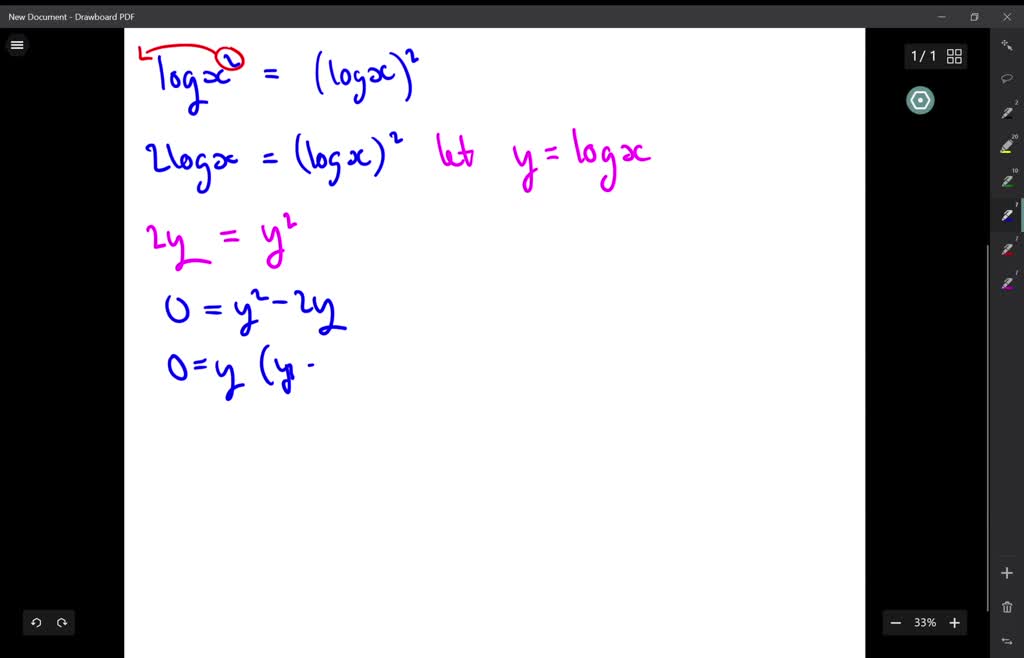
SOLVEDSolve each logarithmic equation. logx^2=(logx)^2
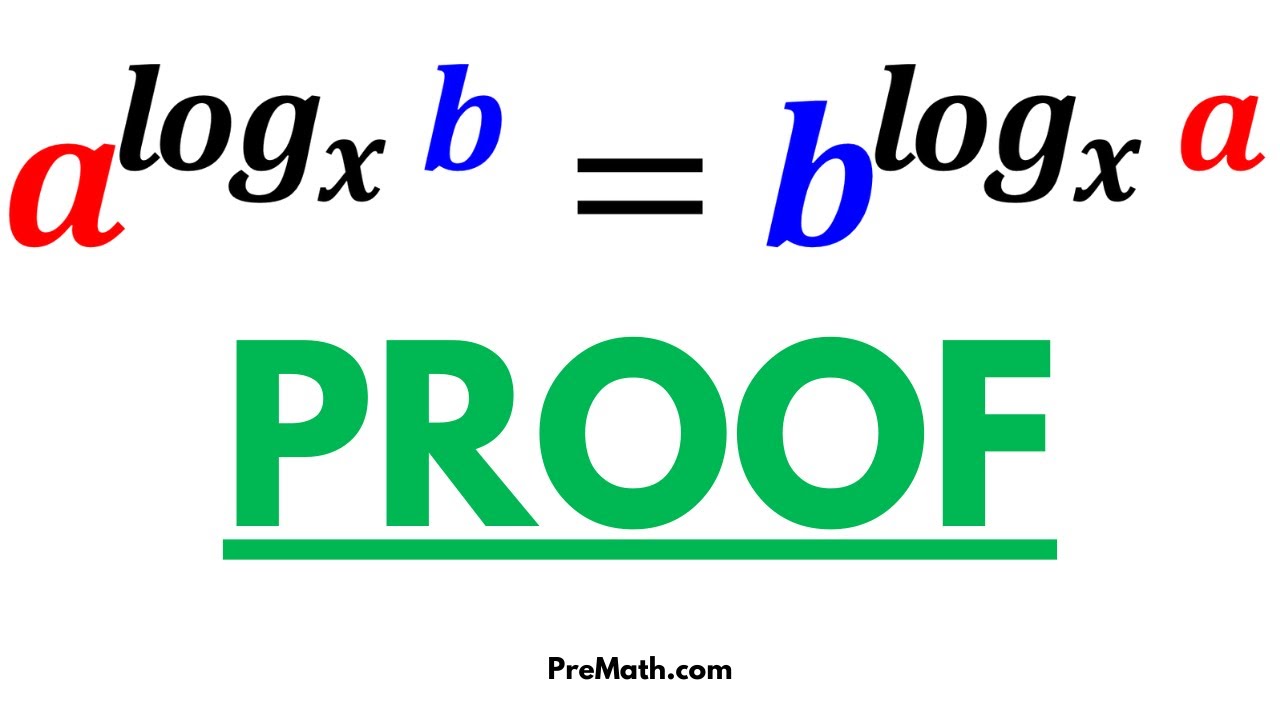
Logarithmic Identity Proof a^logx b = b^logx a StepbyStep Explanation YouTube

a^log x base a=x a^log x base a proof logarithm YouTube

How To Solve For x. Logarithmic Equations YouTube

Chapter 06 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Core Vocabulary Gianna in Algebra 2 part 2
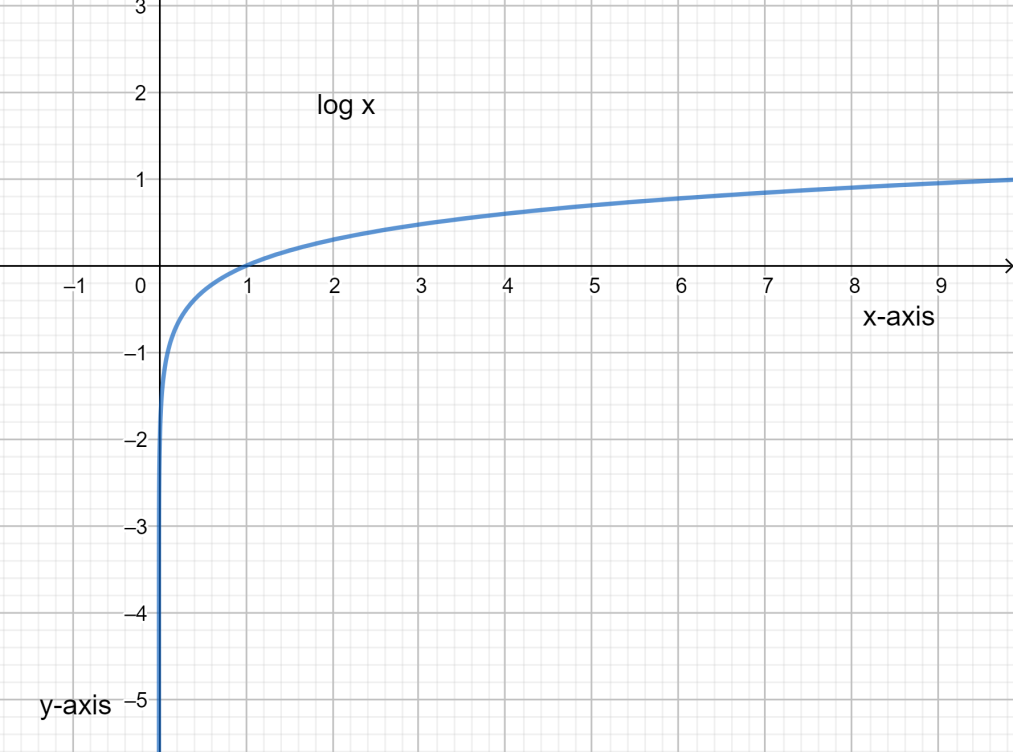
Draw the graph of \\log x